Conditions
This document explains how conditions work within the dialog
system. Conditions determine which actions to execute based on the current context, user input, and conversation history. The system supports two types of conditions: rule-based conditions using context variables and tags, and guideline-based conditions evaluated by AI models.Overview
Conditions in the dialog system determine which actions to execute based on the current context, user input, and conversation history. The system supports two types of conditions:
- Rule-based conditions: Evaluated using deterministic logic with context variables and entities
- Guideline-based conditions: Evaluated using AI models to understand natural language guidelines
Condition evaluation flow
When a node has conditions, the system evaluates them in the following order:
- Conditions are evaluated from left-to-right in their original order as defined in the JSON
- "Else" conditions are automatically moved to the end regardless of their position
- Only the first matching condition (in left-to-right order) is selected and executed
- All other matching conditions are ignored - only one condition's actions are executed
Rule-based conditions
Rule-based conditions use deterministic logic to evaluate context variables, entities, and user input. They are suitable for precise matching scenarios and support three match strategies:
all- All rules must be true for the condition to matchany- At least one rule must be true for the condition to matchelse- Always matches when no other conditions match (fallback)
Supported operators
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
equal | Exact value match | $user.name == "John" |
not_equal | Value does not match | $user.verified != false |
greater | Numeric greater than | $seats > 2 |
less | Numeric less than | $amount < 1000 |
greater_or_equal | Numeric greater than or equal | $seats >= 1 |
less_or_equal | Numeric less than or equal | $amount <= 500 |
contain | String contains substring | $user.email contains "gmail" |
not_contain | String does not contain substring | $user.email not_contain "spam" |
exist | Variable/entity exists | $user.phone exists |
not_exist | Variable/entity does not exist | $payment_method not_exist |
Context variables
Context variables are referenced using the $ prefix:
Entity references
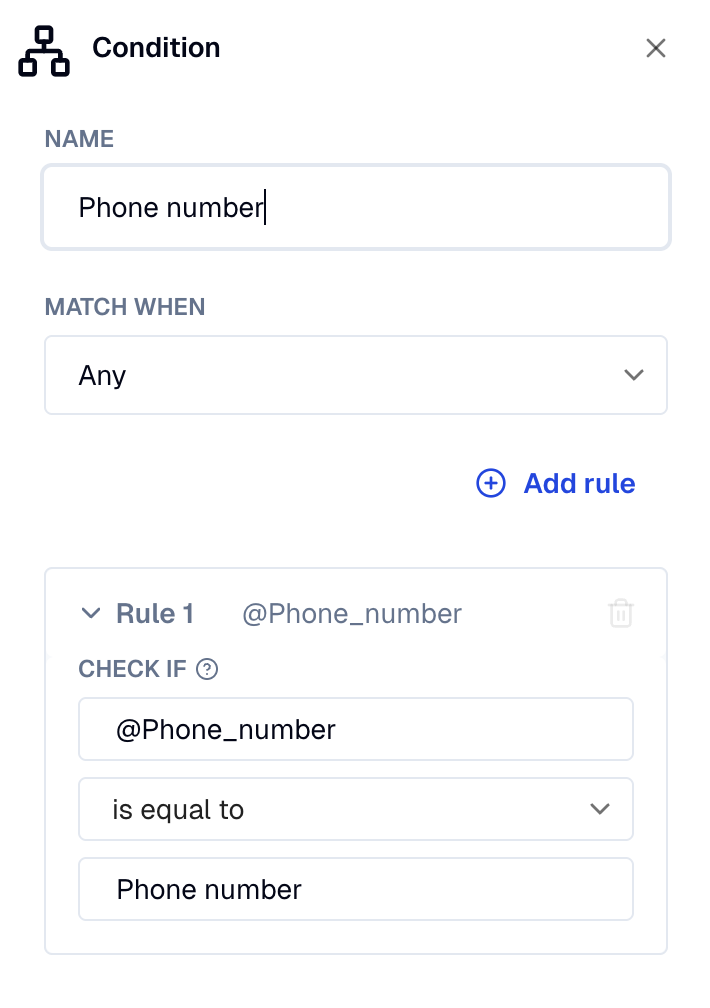
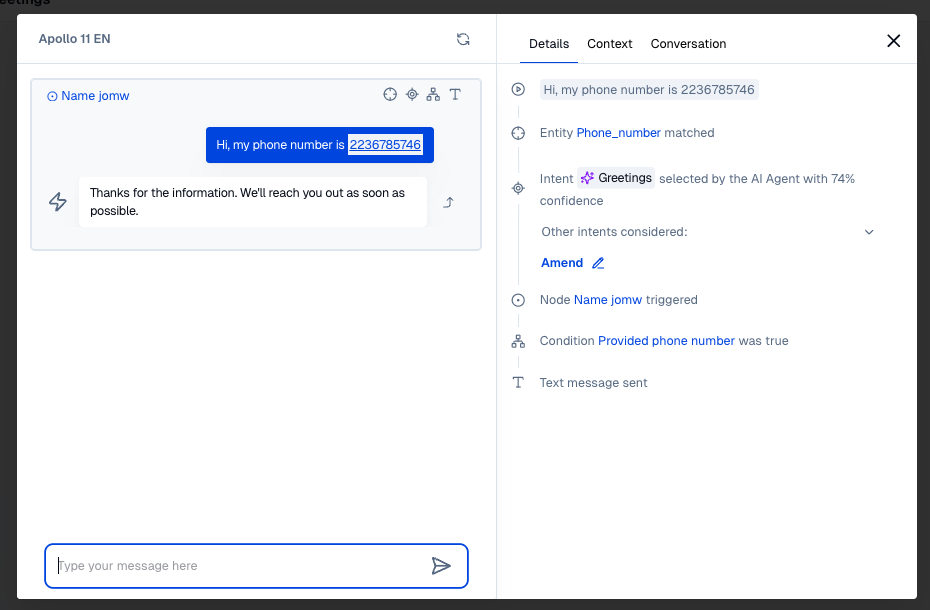
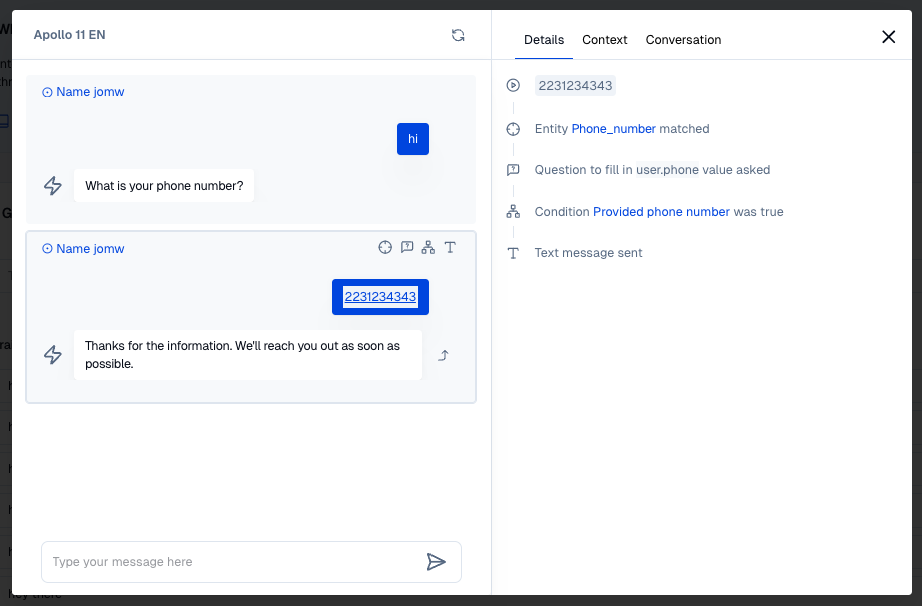
Conditions with entities will match if the user input contains a matching entity. This can be either in the input that triggered the intent node, or if there is a question in a previous step of the same dialog that validates the entity.
From user input are referenced using the @ prefix.
- Entity condition
- Matching entity
- Entity with question
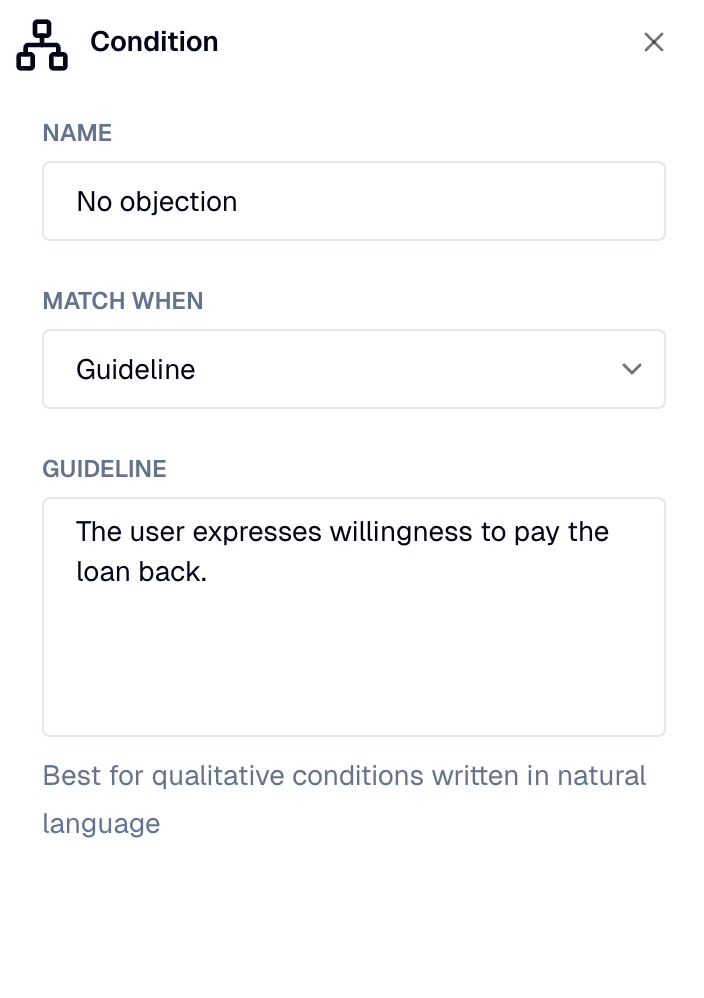
Guideline-based conditions
Guideline-based conditions use AI models to evaluate natural language guidelines against the conversation context. They are flexible and can understand complex scenarios that are difficult to express with rigid rules.
The Condition Evaluator is an AI model that:
- Analyzes the dialog history, context variables, and user input
- Returns matching conditions based on natural language understanding
Used data
The Condition Evaluator sends the following to the AI model:
- Context Variables: All relevant context data (user info, session data, etc.)
- Live Instructions: Special variables to dynamically change the AI Agent's behavior
- Dialog History: Recent conversation turns
- User Question: The current user input
- Guideline Conditions: All available conditions as multiple choice options
Mixed conditions
Nodes can contain both rule-based and guideline-based conditions. The system evaluates them separately and combines the results.
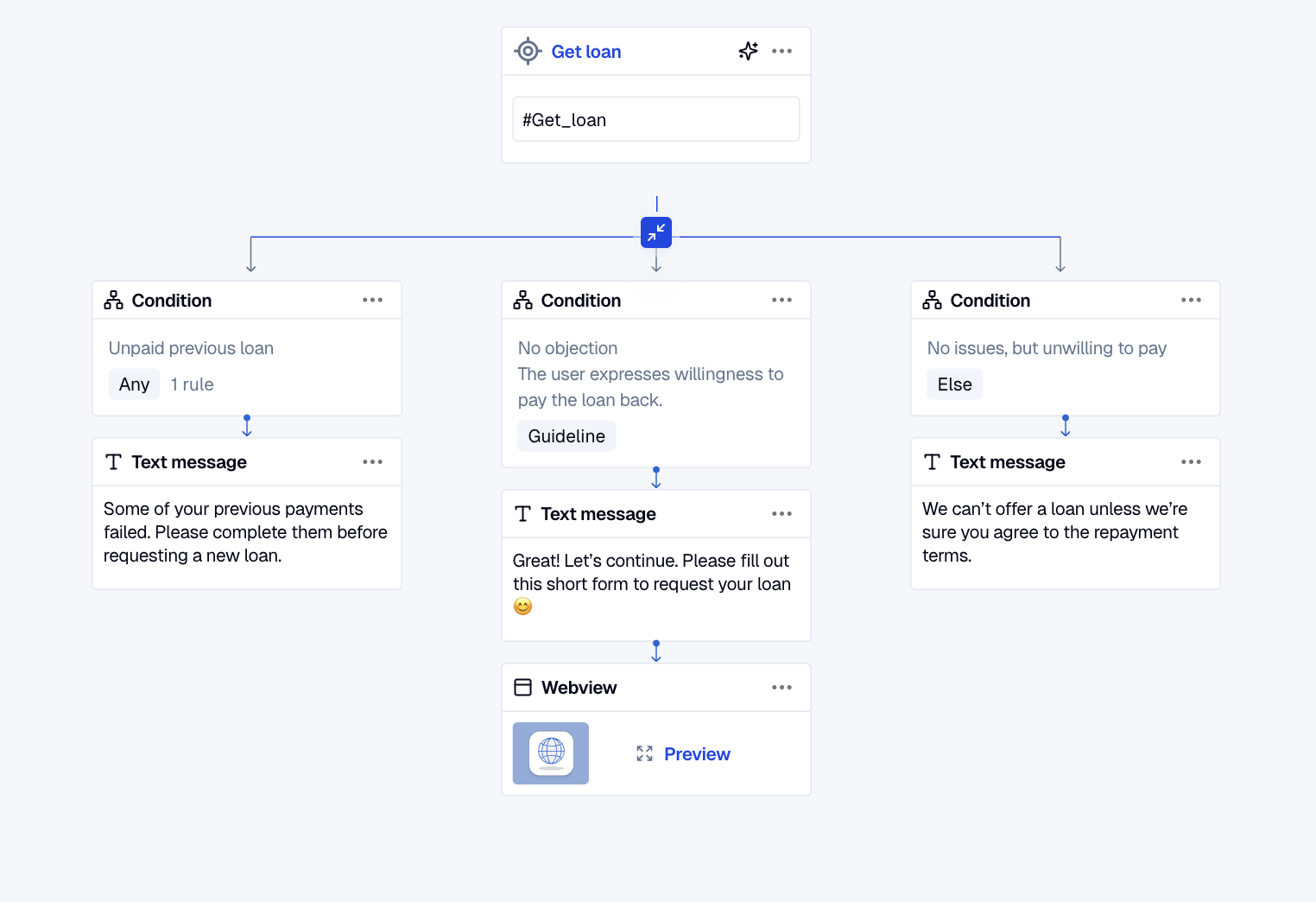
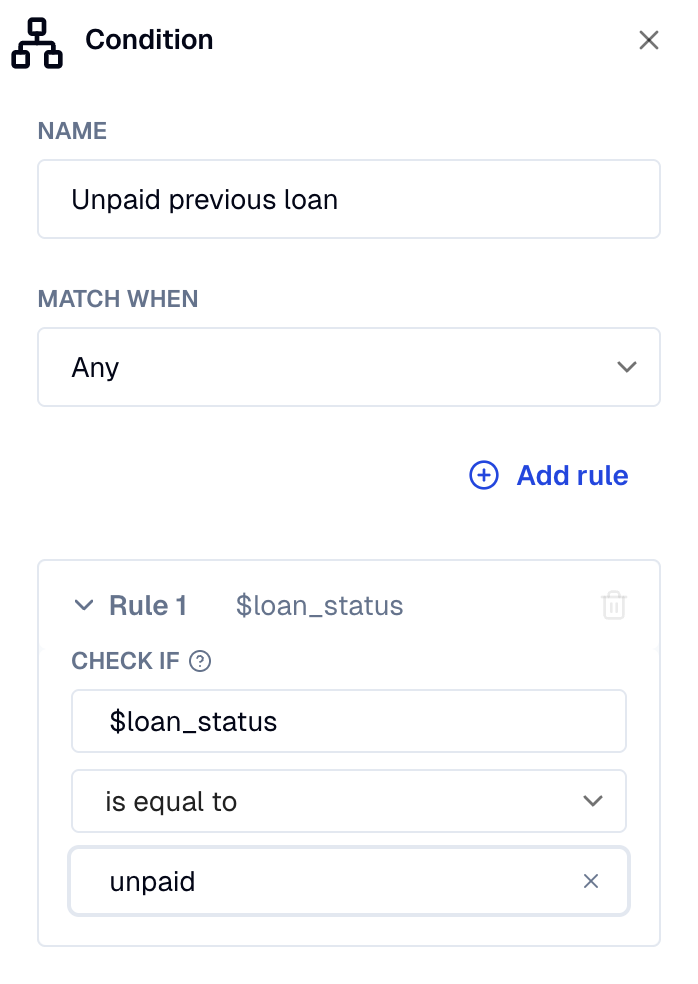
Use case: Loan request – Rule vs guideline conditions
This example shows how to combine rule-based and guideline-based conditions to handle a user requesting a loan.
-
A rule-based condition checks if the variable
$loan_statusis equal to"unpaid". If true, it blocks the loan request and shows a message asking the user to settle their debt first. -
If the rule-based condition does not match, a guideline-based condition is evaluated next. It uses an AI model to detect if the user expresses willingness to repay the loan (e.g., "I can pay monthly"). If matched, the system allows the user to proceed.
-
If neither condition matches, an else condition acts as a fallback. It's used when the user doesn't show a clear intent to repay, and blocks the request.
Condition priority
The system will evaluate the conditions and execute the actions for the first condition that matches. When multiple conditions match:
- Left-to-right ordering - Conditions are evaluated in the order they appear
- First match wins - The first matching condition is executed
Best practices
Rule-based conditions
- Use for precise, deterministic logic
- Use
exist/not_existfor optional data - Template values with
{{$variable}}for dynamic comparisons
Guideline-based conditions
- Use for complex, nuanced scenarios
- Write clear, specific guidelines
- Avoid ambiguous language
- Test with various conversation scenarios
General
- Always include an
elsecondition as fallback - Order conditions by priority (most specific first)
- Monitor condition evaluation performance and accuracy